Insulin and Glucagon | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y9Bdi4dnSlg
In this lesson, you will learn about how your blood glucose level is regulated (or controlled) by two important hormones – insulin and glucagon, via a negative feedback system.
When you consume a meal that is high in carbohydrates, such as rice, pasta, and bread, this will cause your blood glucose level to increase.
Carbohydrates are essentially long chains of repeating glucose monomer units, much like beads on a necklace.
During digestion, this is broken apart into glucose, which absorbed into our bloodstream.
This increased blood glucose level causes a gland known as the pancreas to secrete a hormone called insulin.
Remember that a gland secretes hormones which act on specific target organs.
In this case, the target organ is your liver, which is stimulated to convert glucose to glycogen.
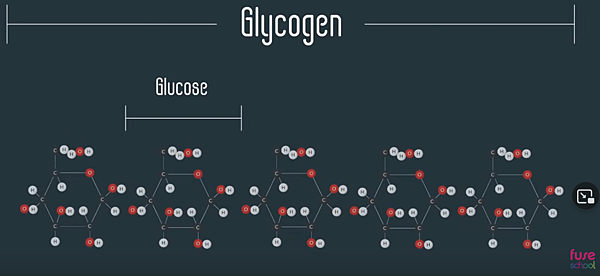
Glycogen is basically long, multi-branched chains of glucose monomers, stored in liver and muscle cells.
Insulin also causes your body cells to uptake (or take in) glucose.
So this decreases your blood glucose level back to its optimal state.
When this system is faulty, this leads to a medical condition known as diabetes – If you want to learn more about diabetes, this will be addressed in another video.
The same response also occurs when you consume foods and drinks high in sugar such as sweets, cakes, and fizzy drinks.
When your blood glucose level drops, such as when you are hungry, the pancreas secretes a hormone called glucagon.
Like insulin, the target organ for glucagon is also the liver, though it stimulates the opposite process – the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
This increases your blood glucose level back to its optimal state.
So to review, insulin and glucagon are two hormones released by the pancreas, which act on the liver to regulate our blood glucose level.
glucagon
n
uk /ˈɡluː.kə.ɡɒn/ us /ˈɡluː.kə.ɡɑːn/
→ a hormone produced in the pancreas that helps glucose (= a type of sugar) to get into the blood
Insulin helps sugar come down; Glucagon helps sugar go up.
carbohydrate
碳水化合物
monomer
單體
gland
腺體
glycogen
n.
uk /ˈɡlaɪ.kəʊ.dʒən/ us /ˈɡlaɪ.koʊ.dʒən/
→ a substance found in the liver and muscles that stores carbohydrate and is important in controlling sugar levels in the blood
糖原(存在於動物的肝臟和肌肉中,儲藏碳水化合物,控制血糖水準)
faulty
a.
uk /ˈfɒl.ti/ us /ˈfɑːl.t̬i/
→ A faulty machine or device is not perfectly made or does not work correctly.
diabetes
n
uk/ˌdaɪ.əˈbiː.tiːz/ us /ˌdaɪ.əˈbiː.t̬əs/
→ a disease in which the body cannot control the level of sugar in the blood
糖尿病



 留言列表
留言列表

